Introduction
With a rapidly growing population and increasing urbanization, India faces significant challenges in ensuring food security while preserving natural resources. Vertical farming, an innovative approach to agriculture, is emerging as a sustainable solution. By growing crops in vertically stacked layers within controlled environments, vertical farming significantly reduces land use, minimizes water consumption, and enhances crop yield.
Recent advancements in hydroponics, aeroponics, and controlled environment agriculture (CEA) have made vertical farming more cost-effective and accessible. This article explores the latest developments in vertical farming techniques, their impact on India’s agricultural landscape, and their potential to revolutionize food production.
Understanding Vertical Farming
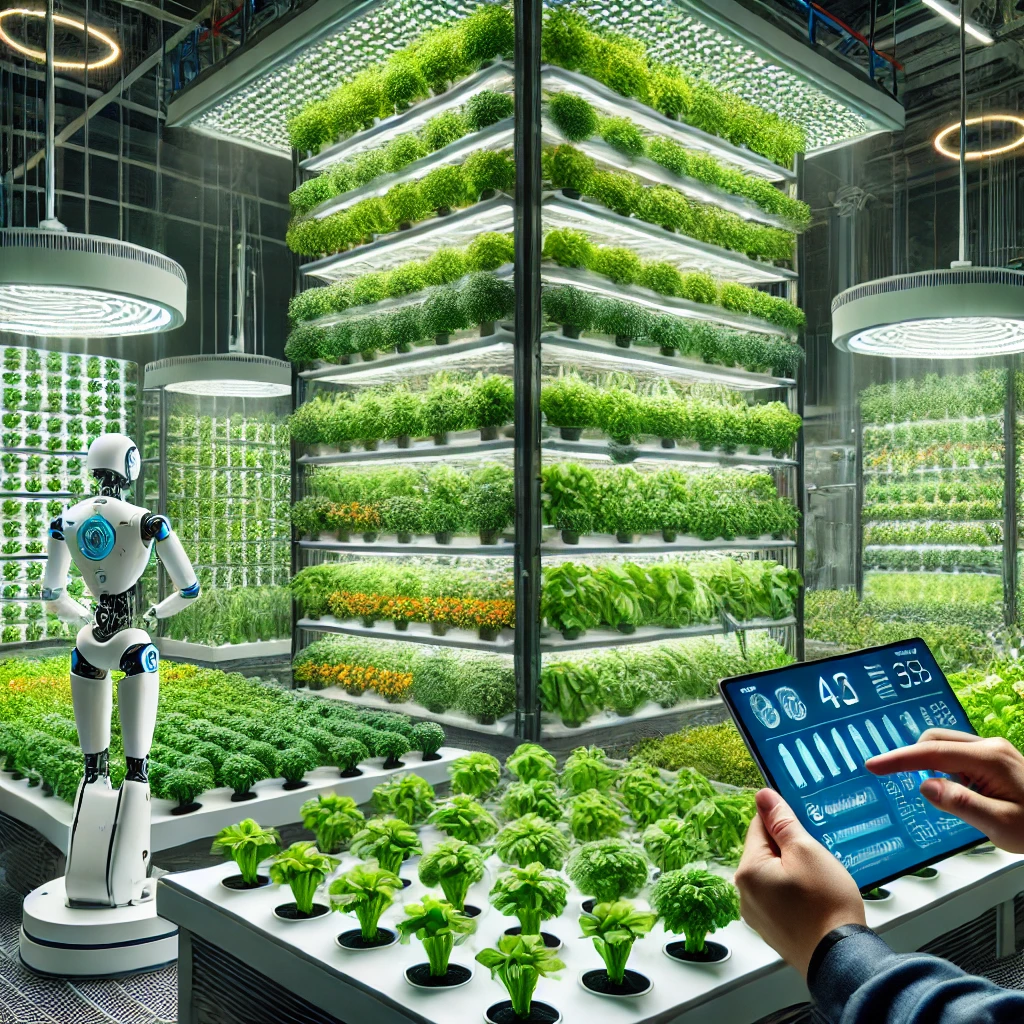
Vertical farming is an advanced agricultural technique that involves growing crops in vertically stacked layers, typically in indoor facilities, greenhouses, or repurposed urban spaces. The controlled environment allows for optimized growth conditions, including temperature, humidity, and light exposure. The main types of vertical farming techniques include:
- Hydroponics: Soil-free cultivation where plants grow in nutrient-rich water solutions.
- Aeroponics: Roots are suspended in the air and misted with nutrient solutions.
- Aquaponics: A combination of hydroponics and fish farming, where fish waste provides nutrients for plants.
Advancements in Vertical Farming Techniques
1. Hydroponic Systems: Optimizing Water and Nutrient Usage
Hydroponics is one of the most widely used techniques in vertical farming due to its water efficiency and controlled nutrient delivery. Recent innovations include:
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT): A thin film of nutrient-rich water continuously flows over plant roots, ensuring optimal absorption.
- Deep Water Culture (DWC): Plant roots are submerged in oxygenated, nutrient-rich water, promoting rapid growth.
- Automated Nutrient Delivery Systems: AI-driven nutrient dispensers adjust pH and nutrient levels in real time, enhancing efficiency.
Impact on India: With increasing water scarcity, hydroponics offers a 95% reduction in water usage compared to traditional farming, making it ideal for India’s drought-prone regions.
2. Aeroponics: Maximizing Space and Resource Efficiency
Aeroponics is a cutting-edge farming technique where plant roots are suspended in the air and misted with a nutrient-rich solution. This method ensures better oxygen absorption, resulting in faster plant growth and higher yields.
- Smart Irrigation Systems: AI-powered misting ensures precise nutrient delivery, reducing waste.
- LED Grow Lights: Energy-efficient lighting optimizes plant photosynthesis while reducing electricity consumption.
- IoT-based Monitoring: Real-time monitoring of humidity, temperature, and nutrient levels improves crop management.
Impact on India: With limited agricultural land, aeroponics enables urban areas to cultivate crops in small, modular units, making it an excellent solution for cities like Mumbai, Delhi, and Bangalore.
3. Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA): Enhancing Productivity
CEA involves using advanced climate control systems, AI-driven automation, and robotics to create ideal growing conditions. Some key developments include:
- Automated Climate Control: AI-based sensors adjust temperature, humidity, and CO₂ levels to optimize plant growth.
- Vertical Stacking Systems: Multi-layered plant shelves increase productivity while reducing land requirements.
- Blockchain Integration: Ensures transparency in food production by tracking plant growth and supply chain logistics.
Impact on India: CEA can help reduce seasonal dependency and ensure year-round crop production, benefiting both farmers and consumers.
Economic and Environmental Benefits of Vertical Farming in India
1. Water Conservation
Traditional farming methods in India consume over 80% of the country’s freshwater resources. Vertical farming techniques like hydroponics and aeroponics reduce water usage by up to 95%, making them crucial for sustainable agriculture.
2. Reduced Land Usage and Urban Farming
India faces rapid urbanization and shrinking agricultural land. Vertical farming allows crops to be grown in urban spaces, rooftops, and abandoned buildings, reducing dependence on rural farmlands.
3. Pesticide-Free Crop Production
Since vertical farms operate in controlled environments, they eliminate the need for harmful chemical pesticides. This results in healthier, organic produce for consumers.
4. Increased Crop Yields
Compared to traditional farming, vertical farming increases crop yields by 3–5 times per square meter. AI-driven automation further enhances productivity by reducing human errors and optimizing growth conditions.
5. Climate Resilience
With unpredictable monsoons and rising temperatures, traditional farming faces increasing challenges. Vertical farming offers a climate-independent solution, ensuring consistent crop production year-round.
Challenges of Vertical Farming in India
Despite its benefits, vertical farming in India faces some challenges:
1. High Initial Investment
Setting up vertical farms requires significant capital for LED lighting, hydroponic/aeroponic systems, and automation. However, government subsidies and private investments are helping reduce costs.
2. Energy Consumption
LED lighting and climate control systems consume large amounts of electricity. Integrating solar energy and energy-efficient technologies can address this issue.
3. Technical Expertise
Farmers need training in hydroponics, IoT systems, and automation. Investing in educational programs and training centers will be essential for widespread adoption.
Government Support and Future Prospects
1. Government Initiatives
The Indian government is actively promoting agri-tech startups and sustainable farming solutions. Some key initiatives include:
- PM-Kisan Yojana: Financial assistance for farmers adopting modern agricultural techniques.
- NABARD (National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development): Funding for sustainable farming startups.
- State Government Programs: Maharashtra, Karnataka, and Telangana have introduced vertical farming subsidies.
2. Startup Ecosystem and Investments
Several Indian startups are revolutionizing vertical farming:
- UrbanKisaan (Hyderabad): Specializing in hydroponic farming for fresh, pesticide-free produce.
- AgriCool (Bangalore): Focused on AI-driven aeroponic farming.
- Future Farms (Chennai): Developing cost-effective hydroponic solutions.
3. Future Growth and Expansion
With growing demand for sustainable and organic food, the future of vertical farming in India looks promising. Expansion into tier-2 and tier-3 cities will make this technology accessible to a larger population.
Conclusion
Vertical farming is revolutionizing agriculture in India by addressing key challenges like water scarcity, land shortages, and food security. Innovations in hydroponics, aeroponics, and controlled environment agriculture are making vertical farming more efficient and scalable.
With government support, increasing investments, and technological advancements, vertical farming has the potential to reshape India’s agricultural landscape, making farming more sustainable, productive, and climate-resilient.
As we move towards a future of urban agriculture, vertical farming will play a crucial role in feeding India’s growing population while preserving our precious natural resources.







+ There are no comments
Add yours