Key Highlights
- Smart Cities Mission Progress: Only 18 out of 100 cities have completed all projects by March 2025, though 94% of 8,067 projects totaling ₹1.64 lakh crore are finished, demonstrating significant infrastructure development
- Satnavari Smart Village Pioneer: India’s first Smart & Intelligent Village launched in Nagpur, Maharashtra with population of 1,800, featuring AI-driven apps, IoT sensors, drone technology, and fiber-optic connectivity
- VoICE Consortium Leadership: 25 Indian technology companies consortium led by R.K. Bhatnagar developed comprehensive rural digitization model integrating smart farming, telemedicine, digital education, and governance systems
- Scalable Implementation Strategy: Maharashtra plans 10 smart villages per taluka, potentially impacting over 3,500 villages statewide, with replication model for nationwide rural transformation
- Technology Integration Success: Smart farming apps provide soil health monitoring, remote irrigation control, weather alerts, plus community drone services for fertilizer spraying and fire emergency response

Smart Cities Mission: A Decade of Progress and Challenges
The Smart Cities Mission, launched in June 2015 with an ambitious vision to transform 100 cities into technology-enabled urban centers, has achieved significant milestones despite facing implementation challenges. With a total investment of ₹1.64 lakh crore, including ₹48,000 crore central funding, the mission has fundamentally reshaped India’s urban landscape. downtoearth
Key achievements as of March 2025 include:
- 94% project completion rate with 7,504 completed projects
- All 100 cities equipped with Integrated Command and Control Centers (ICCCs)
- 84,000+ CCTV cameras installed for public safety
- 17,026 km water supply systems monitored through SCADA technology
- 2,900+ million liters per day drinking water treatment capacity developed
However, only 18 cities have achieved 100% project completion, including Agra, Varanasi, Madurai, Coimbatore, Udaipur, Pune, Surat, and Vadodara. The remaining 82 cities continue working on 559 ongoing projects worth ₹14,239 crore, highlighting implementation complexities.
The Genesis of Smart Villages: Extending Digital Transformation
Recognizing that 65% of India’s population resides in rural areas, the Smart Village concept emerges as a natural evolution of urban digital transformation efforts. Rural India faces multidimensional challenges including limited internet connectivity (29% rural vs 64% urban), traditional farming methods, and inadequate healthcare and educational infrastructure. niralnetworks
The Smart Village initiative addresses these challenges by leveraging cutting-edge technologies to create economically viable, socially inclusive, and environmentally sustainable rural communities. With over 600,000 villages across India, the transformation potential is immense.
Core objectives of Smart Village development include:
- Bridging the digital divide through comprehensive connectivity
- Enhancing agricultural productivity via precision farming
- Improving healthcare access through telemedicine
- Elevating education quality with digital classrooms
- Strengthening governance through e-services

Satnavari: India’s First Smart & Intelligent Village
Satnavari village in Nagpur district, Maharashtra, became India’s pioneering Smart & Intelligent Village following its inauguration by Chief Minister Devendra Fadnavis on August 24, 2025. Located 31 km from Nagpur city with a population of just over 1,800, Satnavari serves as a comprehensive pilot project demonstrating rural transformation potential. pib
The VoICE Consortium, comprising 25 leading Indian technology companies under R.K. Bhatnagar’s leadership, developed and implemented this groundbreaking initiative in collaboration with district administration. The project integrates multiple technological interventions across agriculture, healthcare, education, and governance.
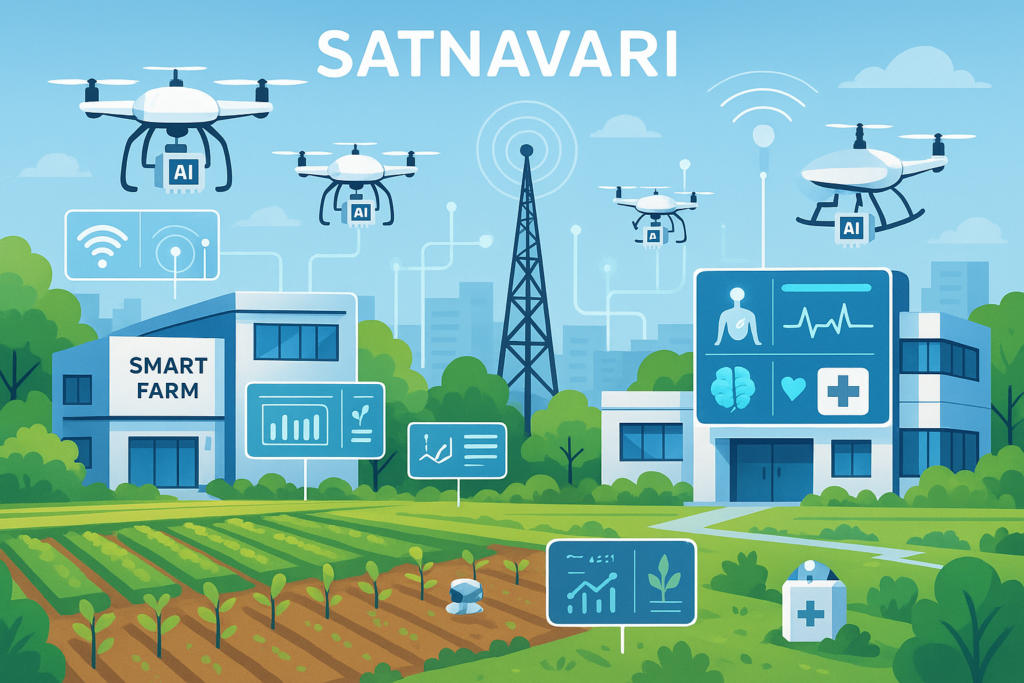
Comprehensive Technology Integration
Infrastructure Foundation:
- Complete Wi-Fi connectivity powered by new tower installation and fiber-optic internet
- Satellite-enabled 4G LTE Network-in-a-Box (NIB) solution
- Solar-powered systems for sustainable energy supply
- High-speed internet access for all residents
Smart Agriculture Implementation:
- Mobile apps providing soil health information, fertilizer recommendations, and water requirement analysis
- Remote irrigation control via smartphone apps activating solar-powered pumps
- Community drone services for fertilizer spraying and fire emergency response
- Real-time weather alerts and crop pattern guidance
- IoT-based soil sensors for precision farming
Healthcare Digitization:
- Telemedicine facilities connecting with Nagpur hospitals
- Remote diagnostic capabilities eliminating need for city visits
- Digital health monitoring systems
- AI-enabled health screening and report transmission
Educational Enhancement:
- Digital classrooms with high-speed internet connectivity
- Educational content delivery from premier institutions
- AI-powered learning platforms
- Remote access to quality educational resources
Technology Components and Implementation Strategy
IoT and AI Integration in Agriculture
The smart farming revolution leverages Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to optimize agricultural productivity while promoting sustainability. Real-time data collection from soil sensors, weather stations, and automated irrigation systems enables precision farming decisions.
Smart farming benefits include:
- 25% yield increase through IoT-based soil and weather sensors
- Significant water savings via optimized irrigation scheduling
- Reduced chemical inputs through targeted fertilizer application
- Enhanced crop surveillance using AI-driven monitoring systems
Punjab case study demonstrates that farmers using IoT-based sensors achieved 25% yield increases and substantial water conservation, validating the scalable potential of smart farming technologies.
Comprehensive Rural Connectivity
Connectivity infrastructure forms the backbone of smart village transformation, requiring robust internet access and reliable power supply. The BharatNet program and MahaNet initiative in Maharashtra laid the foundation through optical fiber deployment across villages.
Connectivity components include:
- 4G LTE Network-in-a-Box solutions for immediate connectivity
- Satellite-enabled communication for remote areas
- Solar-powered infrastructure addressing electricity challenges
- High-bandwidth internet supporting multiple applications simultaneously
Healthcare and Education Transformation
Digital healthcare eliminates geographical barriers through telemedicine platforms connecting rural patients with urban medical expertise. Remote diagnostic capabilities reduce the need for expensive city visits while improving healthcare accessibility.
Educational transformation provides rural students access to premium educational content from top institutions. Digital classrooms equipped with high-speed internet enable interactive learning experiences previously unavailable in remote areas.
Scaling Strategy: Maharashtra’s Ambitious Expansion
Chief Minister Devendra Fadnavis announced plans to develop 10 smart villages in every taluka across Maharashtra, potentially impacting over 3,500 villages statewide. This massive scaling initiative represents one of India’s largest rural digitization efforts.
Implementation strategy includes:
- Taluka-wise phased rollout ensuring systematic coverage
- Local partnership development with district administrations
- Technology standardization for cost-effective deployment
- Capacity building programs for local technical support
Funding and partnership models involve consortium-based approaches combining private sector expertise with government policy support. The VoICE consortium’s success in Satnavari provides a replicable framework for state-wide expansion.
Economic Impact and Development Outcomes
Agricultural Productivity Enhancement
Smart farming technologies demonstrate measurable productivity improvements through data-driven decision making. IoT sensors monitor soil moisture, temperature, pH levels, and nutrient content, enabling precision agriculture that optimizes resource utilization.
Economic benefits include:
- Reduced input costs through optimal fertilizer and water usage
- Increased crop yields via scientific farming practices
- Enhanced crop quality improving market value
- Reduced post-harvest losses through better storage monitoring
Rural Employment Generation
Technology implementation creates new employment opportunities in rural areas, including technical support roles, data analysis positions, and drone operation services. Digital skill development programs prepare rural youth for technology-enabled careers.
Entrepreneurship opportunities emerge through tech-enabled services like precision agriculture consulting, drone-based spraying services, and digital marketing for agricultural products.
Challenges and Implementation Considerations
Infrastructure and Connectivity Barriers
Despite progress, rural connectivity remains challenging due to geographical constraints, power supply limitations, and maintenance difficulties. Satellite-based solutions address some issues but require significant investment and technical expertise.
Key challenges include:
- Intermittent power supply affecting technology operations
- Limited technical support in remote areas
- High initial investment costs for comprehensive infrastructure
- Digital literacy gaps among rural populations
Adoption and Sustainability Issues
Technology adoption requires behavioral change and skill development among rural communities. Training programs and continuous support systems are essential for sustainable implementation.
Sustainability considerations include:
- Long-term maintenance of technical infrastructure
- Cost-effectiveness for small-scale farmers
- Regular technology updates and system upgrades
- Local capacity building for independent operations
Policy Framework and Government Support
National and State Policy Alignment
Smart Village initiatives align with national digitization goals including Digital India, PM-WANI program, and National Mission on Strategic Knowledge for Climate Change. State-level policies provide implementation frameworks and funding mechanisms.
Government support includes:
- Central funding through rural development schemes
- State government infrastructure development
- Public-private partnership models
- Regulatory frameworks for technology deployment
Integration with Existing Programs
Smart Village development integrates with existing rural development programs including MGNREGA, National Rural Health Mission, and Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan, creating synergistic effects and resource optimization.
Future Prospects and Expansion Potential
Nationwide Replication Models
The Satnavari success model provides a blueprint for nationwide replication across India’s 600,000+ villages. State governments can adapt the technology framework to local contexts while maintaining core functionality.
Replication strategies include:
- State-specific customization addressing regional challenges
- Technology cost reduction through economies of scale
- Local manufacturing of IoT devices and sensor systems
- Regional training centers for technical support
Technology Evolution and Innovation
Emerging technologies like 5G connectivity, artificial intelligence, blockchain, and edge computing will enhance Smart Village capabilities. Continuous innovation ensures technology relevance and performance improvement.
Future enhancements may include:
- Advanced AI analytics for predictive farming
- Blockchain-based crop insurance and supply chain transparency
- Virtual reality applications for remote education
- Smart energy grids with renewable energy integration
Global Context and Best Practices
International Smart Village Models
Global examples of rural digitization provide valuable insights for Indian implementation. South Korea’s u-villages, European Union’s smart rural initiatives, and China’s digital village programs demonstrate successful approaches to technology-enabled rural development.
Lessons learned include:
- Community participation importance in technology adoption
- Integrated approach combining multiple sectors simultaneously
- Long-term sustainability planning beyond initial implementation
- Regular monitoring and impact assessment mechanisms
Conclusion
India’s journey from Smart Cities Mission to Smart Villages represents a paradigmatic shift toward inclusive digital transformation. While the Smart Cities Mission achieved significant infrastructure development in urban areas, persistent challenges in complete project implementation highlight the complexity of large-scale technology deployment.
The Satnavari Smart Village demonstrates that rural areas can successfully adopt advanced technologies when provided with appropriate infrastructure and community support. VoICE Consortium’s comprehensive approach integrating agriculture, healthcare, education, and governance creates a holistic development model addressing multiple rural challenges simultaneously.
Maharashtra’s ambitious plan to scale this model to 3,500+ villages represents one of the world’s largest rural digitization initiatives. Success will depend on sustained government commitment, private sector engagement, and community participation in technology adoption.
The economic potential is substantial, with smart farming technologies alone demonstrating 25% yield increases and significant resource savings. Employment generation through technology services and skill development can reduce rural-urban migration while improving living standards.
Challenges including infrastructure limitations, digital literacy gaps, and sustainability concerns require continuous attention and innovative solutions. However, the Satnavari pilot’s early success provides confidence in the model’s viability and scalability.
As India progresses toward its 2047 development goals, Smart Villages offer a pathway for balanced national growth that empowers rural communities while preserving agricultural foundations. The integration of traditional knowledge with modern technology creates sustainable development models that honor cultural heritage while embracing innovation.
🔹 Mains Questions
- GS-II (Governance):
Discuss how the Smart & Intelligent Village initiative in Satnavari reflects a shift in India’s development paradigm from urban-centric smart planning to holistic rural transformation. How can such initiatives bridge the rural–urban divide? - GS-III (Technology & Infrastructure):
Critically evaluate the role of emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and drones in rural governance and service delivery. What are the challenges of scaling such pilots across India?






+ There are no comments
Add yours