Key Highlights
- NavIC provides 5-10 meter accuracy within India, significantly better than GPS’s 20-meter precision in the region
- Seven satellites constellation with three geostationary and four geosynchronous satellites ensuring continuous coverage
- Mandatory smartphone integration by January 2025 for 5G devices and December 2025 for all phones
- Born from Kargil War lessons when US denied GPS access, highlighting the need for strategic autonomy
- Dual-service architecture offering Standard Positioning Service for civilians and Restricted Service for defense
From Kargil’s Bitter Lesson to Strategic Innovation
The story of Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC) begins with a stark reminder of technological dependence during the 1999 Kargil War. When Indian forces desperately needed GPS data to track enemy positions in the treacherous Kargil region, the United States denied access to its Global Positioning System. This denial exposed India’s vulnerability in critical military operations and catalyzed the vision for an indigenous navigation system.
Developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), NavIC represents India’s answer to foreign-controlled navigation systems. The system became operational in 2018, marking a significant milestone in India’s journey toward technological self-reliance. Unlike global systems such as GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou, NavIC is specifically designed as a regional system covering India and extending up to 1,500 km beyond its borders. isro.gov
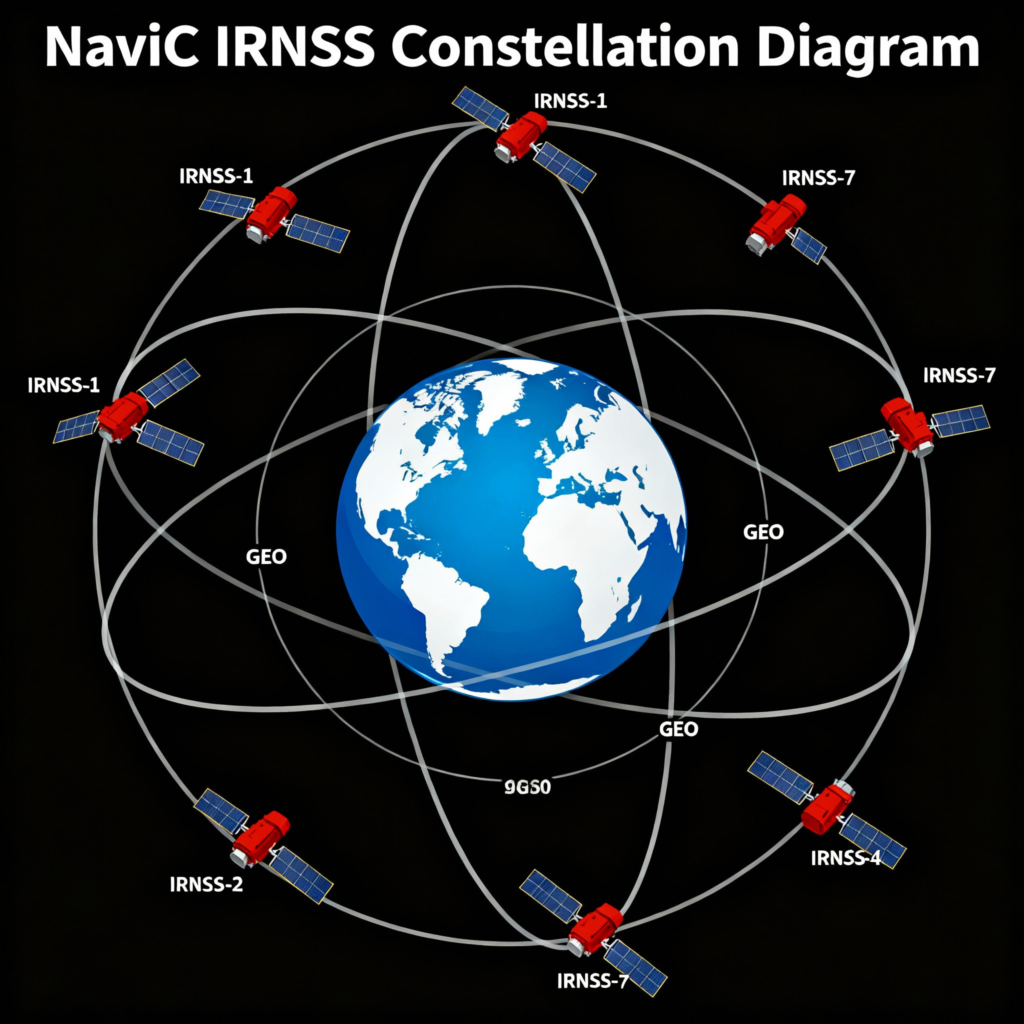
Technical Architecture: Seven Satellites, Infinite Possibilities
NavIC operates through a sophisticated constellation of seven satellites strategically positioned in different orbital configurations. Three satellites are placed in geostationary orbit (GSO) at 32.5°E, 83°E, and 129.5°E, while four satellites occupy inclined geosynchronous orbit (GEO) with equatorial crossings at 55°E and 111.75°E. IRNSSProgramme
The system utilizes dual-frequency signals – L5 band (1176.45 MHz) and S-band (2492.028 MHz) – providing enhanced accuracy and resistance to ionospheric disturbances. This technical design ensures position accuracy better than 20 meters for civilians and even higher precision for authorized military users through the Restricted Service.
The ground infrastructure comprises control centers, precise timing facilities, range and integrity monitoring stations, and two-way ranging stations operating around the clock. With 16 IRIMS (IRNSS Range and Integrity Monitoring Stations) currently operational, the system maintains continuous monitoring and precise timing accuracy of 2 nanoseconds.
Strategic Significance: Beyond Navigation
Defense and Security Applications
NavIC’s strategic importance transcends basic navigation services. The system provides encrypted Restricted Service (RS) for the Indian Armed Forces, offering sub-5-meter accuracy crucial for precision military operations. The system has been integrated with defense platforms including BrahMos missiles, UAVs, and border surveillance systems.

Recent developments suggest NavIC played a crucial role in precision military operations, with reports indicating 2-meter accuracy in strategic strikes. The system’s independence from foreign control ensures uninterrupted service during conflicts, addressing the vulnerability exposed during the Kargil War. stratheia
Economic and Technological Benefits
NavIC reduces India’s dependence on foreign satellite systems, estimated to save millions of dollars in licensing fees while building indigenous technological capabilities. The system supports various civilian applications including transportation, logistics, disaster management, and precision agriculture.
Government Mandates and Market Integration
The Indian government has implemented mandatory NavIC support in smartphones, with specific timelines established for different device categories. All 5G smartphones must support NavIC by January 1, 2025, while other devices have until December 2025 for compliance.

This mandate extends beyond smartphones to include automotive navigation systems and IoT devices. The government plans to offer additional incentives under the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for manufacturers using India-designed chips supporting NavIC technology.
Major smartphone brands including Xiaomi, OnePlus, Vivo, Realme, and Apple have already integrated NavIC support in select models. Apple’s inclusion of NavIC in iPhone 15 models represents a significant validation of the system’s global competitiveness.
Applications Across Sectors
Agriculture and Rural Development
NavIC enables precision farming through accurate field mapping, crop monitoring, and resource optimization. Farmers can utilize the system for land measurement, boundary mapping, and precision application of fertilizers and pesticides, potentially increasing agricultural productivity significantly.

Disaster Management and Emergency Response
The system’s regional accuracy of 5-10 meters proves crucial during natural disasters including earthquakes, cyclones, and floods. NavIC assists in search and rescue operations by providing precise coordinates, enabling efficient deployment of emergency resources and coordination of relief efforts.
Transportation and Logistics
NavIC supports navigation for the logistics and transportation industry, improving delivery efficiency and route optimization. Maritime navigation benefits from the system’s coverage in the Indian Ocean region, enhancing safety and tracking capabilities for vessels.
Current Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its strategic importance, NavIC faces significant operational challenges. Currently, only four of 11 satellites are fully operational, with several experiencing technical failures or orbital positioning issues. The recent NVS-02 satellite failure to reach its intended orbit highlights ongoing technical challenges.
However, ISRO plans to launch NVS-03, NVS-04, and NVS-05 by 2026 to complete the second-generation constellation. These new satellites incorporate L1 band signals and indigenous atomic clocks, improving compatibility with consumer devices and enhancing overall system reliability.
Global Positioning and Diplomatic Impact
NavIC positions India as a space power and enhances the country’s role as a net security provider in South Asia. The system aligns with India’s “Neighborhood First” policy and offers potential for data-sharing cooperation with SAARC nations and Indian Ocean Region countries.
The system’s recognition by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) as part of the World Wide Radio Navigation System (WWRNS) enhances India’s global maritime influence. This recognition facilitates international adoption and strengthens India’s position in global navigation services.
NavIC vs. Global Systems: Competitive Advantages
Compared to GPS, NavIC offers superior accuracy within the Indian region – achieving 5-10 meter precision versus GPS’s 20-meter accuracy. The system provides faster Time To First Fix (TTFF) and better performance in urban environments due to its regional optimization.
NavIC’s dual-frequency signals better compensate for ionospheric delays, particularly important in India’s tropical climate. The system’s always-visible satellites for the Indian region ensure consistent signal strength and availability.
Looking Ahead: Vision 2030 and Beyond
NavIC’s future roadmap includes expansion from regional to global coverage through the proposed Global Indian Navigation System (GINS) with 24 satellites. This ambitious project would position India alongside major space powers with comprehensive global navigation capabilities.
The system’s integration with emerging technologies including 5G networks, IoT devices, and autonomous vehicles will drive innovation across sectors. Enhanced accuracy through ground-based augmentation systems and international cooperation will further strengthen NavIC’s capabilities.
As India continues investing in space technology and digital infrastructure, NavIC stands as a testament to the country’s growing technological prowess and strategic vision. The system not only addresses immediate security concerns but also positions India as a leader in space-based services for the 21st century.









+ There are no comments
Add yours