Cracked roads and recurring potholes have long been the bane of drivers and city planners. Enter glass grid pavement technology—an innovative solution reshaping the future of modern roadways by enhancing their structural resilience, reducing maintenance needs, and delivering longer-lasting, smoother journeys.
What is Glass Grid Pavement Technology?
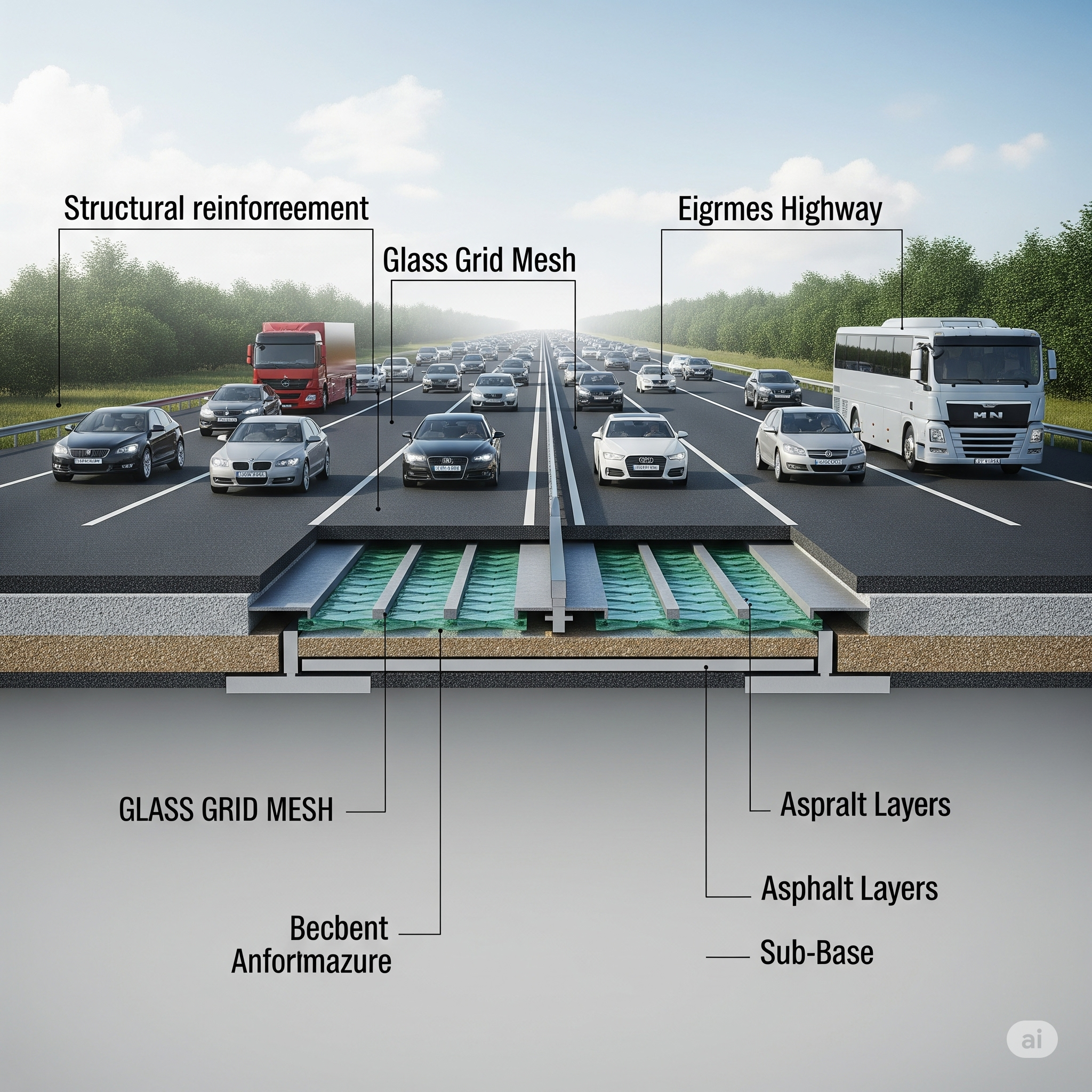
At the core of this breakthrough is a durable fiberglass (glass grid) mesh embedded within the pavement’s layers. Much like steel rebar in concrete, this grid reinforces asphalt but with added benefits, especially against crack formation and water damage.
How Glass Grid Works
- Load Distribution: The mesh spreads the force from traffic, minimizing localized failure.
- Crack Resisting: It interrupts and slows crack propagation by providing a continuous reinforcement throughout the pavement.
- Moisture Defense: The structure helps prevent water from infiltrating and undermining road layers.
- Corrosion Resistant: Unlike metallic reinforcements, fiberglass doesn’t rust, making it ideal for diverse climates.
Why Do Roads Crack and Potholes Form?
- Repeated Traffic Loads: Especially from heavy vehicles, which fatigue the pavement.
- Temperature Extremes: Expansion/contraction during heat/frost cycles.
- Water Ingress: Moisture entry accelerates base layer erosion.
- Material Aging: Asphalt once oxidized becomes brittle and susceptible.
Advantages of Glass Grid Reinforcement
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Longevity | Extends road life by up to 1.5–2 times compared to traditional pavement. |
| Fewer Repairs | Reduces maintenance frequency and the need for expensive overlays. |
| Cost Efficiency | Initial investment offset by huge long-term savings on repairs and resurfacing. |
| Environmental Benefits | Less repair work means fewer emissions, reduced use of raw materials, and less traffic disruption. |
| Adaptability | Effective in new builds and pavement rehabilitation/resurfacing projects. |
How is the Glass Grid Installed?
- Surface Prep: Clean and level the road base.
- Grid Placement: Roll out the glass grid onto the surface.
- Bonding Layer: Apply a tack coat to bond the grid with the new asphalt overlay.
- Overlay Application: Hot asphalt mix is laid and compacted over the grid.
- Finishing: Cool and inspect before reopening to traffic.
Environmental and Economic Impact
- Reduces Greenhouse Emissions: Fewer repairs mean less machinery and material transport.
- Conserves Resources: Lowers demand for new asphalt and aggregates.
- Cuts Public Spending: Decreases recurring repair costs, enabling better use of infrastructure budgets.
Global Adoption and Results
- US Case Study: Highways in North Carolina using glass grid reported an 80% reduction in reflective cracking after seven years.
- UK Trials: Motorways with glass grid overlays have longer resurfacing intervals and smoother rides.
- Asia’s Expansion: Glass grid reinforcement is being piloted in India and China amid rapid urban growth due to its cost advantage and performance.
Challenges and The Road Ahead
While glass grid systems are costlier upfront, the life-cycle savings and safety improvements outweigh the initial expense. Future trends:
- Integration with smart sensors.
- Use with recycled road materials.
- Expansion to runways and urban transits.
Conclusion: Paving the Way to Tomorrow
Glass grid pavement technology is more than a clever engineering solution—it’s a shift toward smarter, longer-lasting, and more sustainable transportation infrastructure. As urbanization and climate stresses increase, adopting robust and innovative materials becomes not just cost-effective but essential. The vision of crack-free, pothole-resistant highways is no longer just a dream—it’s taking shape under our wheels. As this technology proliferates, we can all look forward to safer, smoother, and more dependable journeys for decades to come.








+ There are no comments
Add yours